How AI Agents Actually Collaborate: Real-World Workflows, Protocols, and Pitfalls
Written by - Millan Kaul
Where protocols weave and memory lingers, AI agents quietly shape the world—unseen, but always at work together.
Artificial intelligence agents are increasingly orchestrating real-world tasks behind the scenes—but how do they actually work together? This post bridges the gap between foundational AI protocol concepts (like MCP, session memory, or workflow automation) and their practical use in actual product and business workflows.
Key Concepts and Why They Matter
- Agent-to-Agent Protocols (A2A): Let distributed AI modules directly exchange information and coordinate roles.
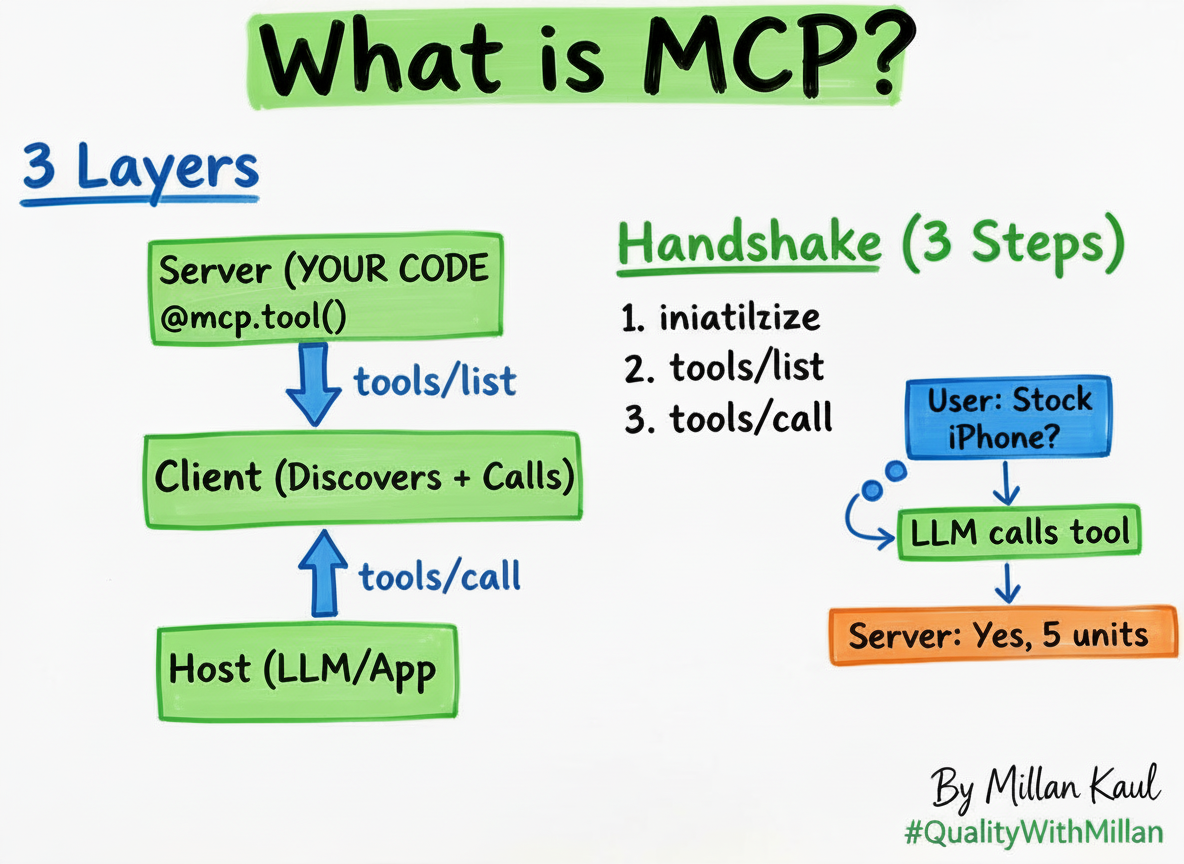
- Model Context Protocol (MCP): Standardizes how agents share context, invoke tools, and retain seamless state management.
- Session Memory: Ensures agents “remember” what’s been discussed or processed, even across different channels and hand-offs.
- Workflow Automation: Allows multiple agents to dynamically sequence tasks with error handling, retries, and escalation if needed.
Real-World Example: Order Fulfillment in E-Commerce
Let’s demystify this with an order fulfillment use case:
Scenario:
A customer places an online order for a smartphone and accessory; the goal is to confirm payment, check inventory, and arrange delivery.
Step-by-Step AI Agent Workflow (simplified)
- Order Orchestrator Agent (receives order)
- Initializes a unique session and places the request into the MCP framework.
- Inventory Agent (checks stock)
- Called via MCP by the Order Orchestrator. If all items aren’t available, the agent relays the result using the A2A protocol.
- Payment Agent (executes transaction)
- Triggered next if inventory is good. If payment fails, the session context and response are routed for retry or escalation.
- Delivery/Logistics Agent (schedules shipment)
- Once payment clears, the orchestrator invokes this agent. This agent also updates notification channels via API integration.
- Notification Agent (updates user)
- Sends confirmation, order tracking, and alerts via email/SMS—all using context stored and relayed by MCP.
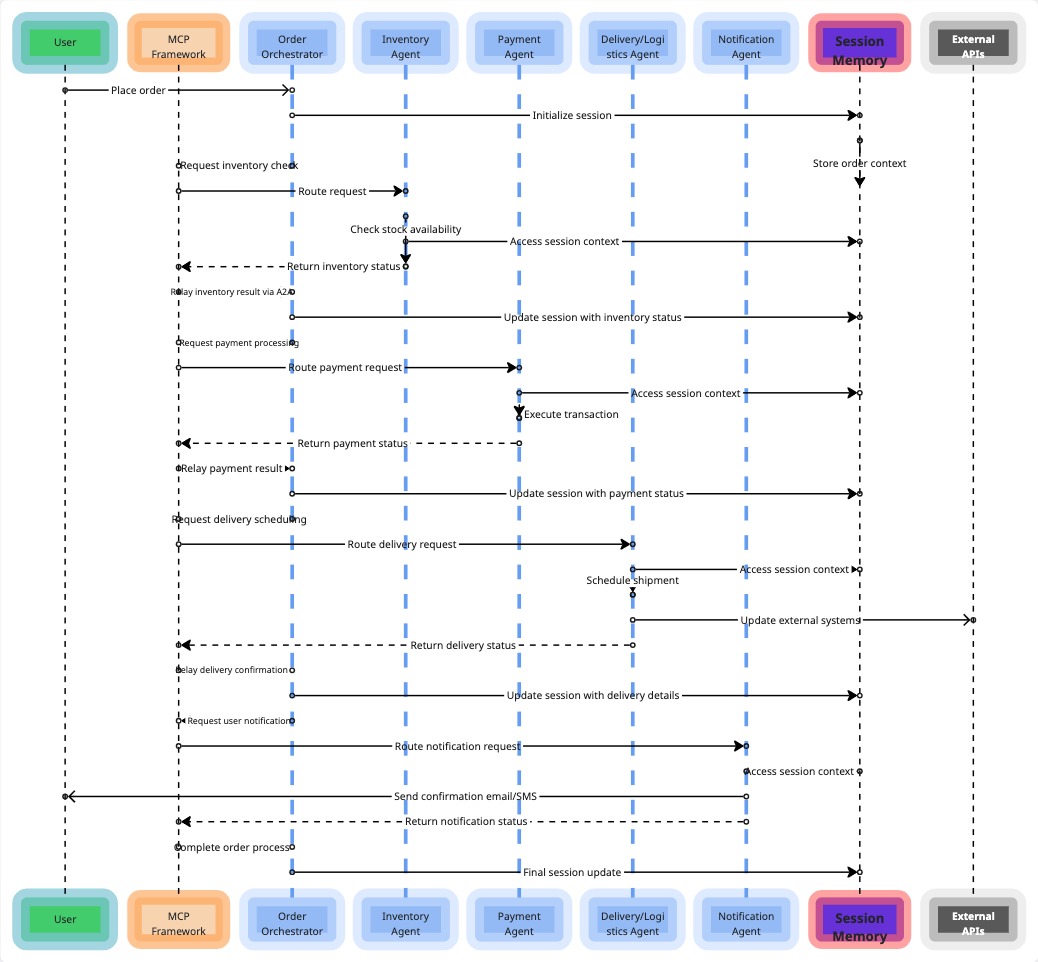
Above Visual is workflow Sequence Diagram, showing
- A layered flow showing each
“Agent”as a block. - Arrows illustrate message passing (via
MCPandA2A). Session memory(context/state) is visualized as a connected thread running (kind) parallel to the workflow.
What Can Go Wrong? Common Pitfalls
❌ Losing context between steps if session memory isn’t consistent.
❌ Agents “misunderstand” message order due to poor protocol design.
❌ Real-world APIs might fail, so proper error and retry logic in orchestrators is crucial.
❌ Security and authorization: Make sure only the right agents can invoke sensitive actions.
So, what is the Key Takeaway ?
Possibly, the next time you click Order or reset a password, there’s a high chance multiple AI agents, empowered by standards like MCP, are collaborating to deliver the seamless result—quietly orchestrating the magic behind every modern digital workflow.
Deeper Dive Reference Links
- AI Agent Protocols Explained - IBM
- How to Build an AI Agent That Automates Real-Estate Lead Generation - Intuz
- How MCP Orchestrates Complex Multi-Agent Systems - Dynatrace
- Unpacking Qualys Agentic AI: Technical Insights into Its Architecture and Capabilities
Want to learn more❓
Follow Quality With Millan or Share it on LinkedIn