Exponential backoff strategy - explained with {code}
Written by - Millan Kaul

Let me start with a simple explanation from a common situation. Let’s say there is a smartphone app which is failing to connect to server ( back-end), it might try again 1 second later, then if it fails again, 2 seconds later, then 4, etc.. Each time the pause is multiplied by a fixed amount (in this case 2).
1. What is Exponential backoff ?
The Exponential Backoff is a technique used to handle retries in a more intelligent and efficient manner.
It involves progressively increasing the time between retries after encountering a transient error, such as a 500 Internal Server Error, in an API response.
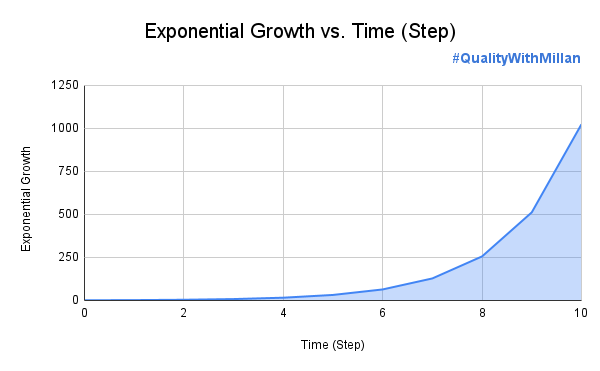
The delay between retries grows exponentially, typically doubling with each retry attempt, like this graph below.
2. Why use of Exponential backoff strategy ?
The need for the Exponential backoff strategy stems from the unpredictable nature of network communications and server responses. Transient errors, such as temporary network issues or server overloads, can occur sporadically and may resolve themselves given time.
By implementing an exponential backoff approach, we can reduce the load on servers during error spikes and increase the chances of successful retries.
Let me give you two real life examples:
-
BLACK FRIDAY SALE [e-commerce] : A e-commerce platform with a checkout API endpoint. During peak hours, the server occasionally returns
500errors due to high traffic. Implementing an Exponential Backoff Strategy in your API client helps alleviate server load by intelligently retrying failed requests with increasing delays. This ensures smoother checkout experiences for users during busy periods 🛍️ 🛒 . -
In system resilience testing, simulate network fluctuations 📈 📉 by introducing intermittent delays and errors in API responses. Use the Exponential Backoff Strategy to model varying network conditions, such as increased latency or sporadic connection failures. This helps evaluate how well the system recovers and maintains functionality under adverse circumstances, enhancing overall resilience.
3. Implementation Example
Let me show you a simple JavaScript implementation example.
const axios = require('axios');
async function fetchDataWithExponentialBackoff() {
const apiUrl = 'https://qualitywithmillan.github.io';
const maxRetries = 5;
let retryCount = 0;
let delay = 1000; // Initial delay of 1 second
while (retryCount < maxRetries) {
try {
const response = await axios.get(apiUrl);
break;
} catch (error) {
console.log(`Retrying in ${delay} milliseconds...`);
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, delay));
delay *= 2; // Exponential increase in delay
retryCount++;
}
}
if (retryCount === maxRetries) {
console.error('Failed: Max retry limit reached.');
}
}
fetchDataWithExponentialBackoff();
So, if you ask me to explain in 1 line of code, thi is the key?
// Exponential backoff strategy in 1 line
delay = Math.min(delay * 2, maxDelay);
So, that’s it!
But!
But!!
But!!!
should we implement all the time?
4.  When Not to use Exponential backoff?
When Not to use Exponential backoff?
While the Exponential Backoff Strategy is effective for transient errors, it may not be suitable for all error types. Let me share few examples.
-
For critical errors that require immediate attention or errors indicating permanent issues, such as authentication failures or invalid requests, a different error-handling approach should be employed.
-
Resource Utilization: Continuous retries with exponential delays consume system resources, such as CPU and memory, which may impact overall system performance and scalability.
-
Additionally, for real-time systems or time-sensitive operations, excessive retries with exponential delays may not be feasible.
e.g In a share trading app handling transactions, certain errors like authentication failures or validation errors should not be retried using an Exponential Backoff Strategy.
Immediate user feedback or intervention is required in such cases to prevent potential security risks or incorrect data processing. These errors should be handled with appropriate error-handling mechanisms instead of retries.
Once again :
The purpose of using an exponential backoff strategy is to prevent overwhelming the API server with rapid retry attempts when it returns a 5xx error. By increasing the delay between retries exponentially, the load on the server is reduced, and it gives the server more time to recover from the error before the next retry attempt.
Further reading and references:
Want to learn more❓
Follow Quality With Millan or Share it on LinkedIn